Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis is a type of eczema (atopic dermatitis) caused by a reaction to an allergen. Unlike irritant contact dermatitis, which occurs at the time of the allergen touching the skin, contact dermatitis occurs around 24-72 hours after exposure. The most common allergens causing allergic contact dermatitis often change over time, as certain chemicals come in or out of use in the manufacture of products that come in contact with the skin. Most recently, common causes of allergic contact dermatitis include nickel, chromates, rubber chemicals, and neomycin. Frequent sensitizers in the general population also include fragrance, formaldehyde, lanolin (wool grease found in ointments and cosmetics), and many other common environmental chemicals.
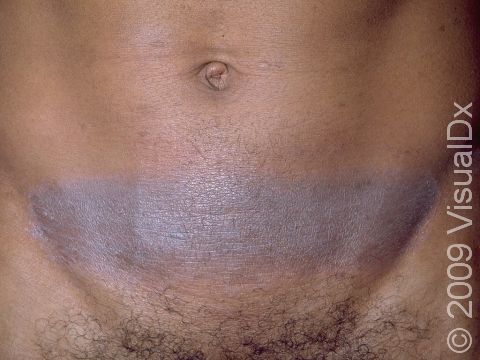
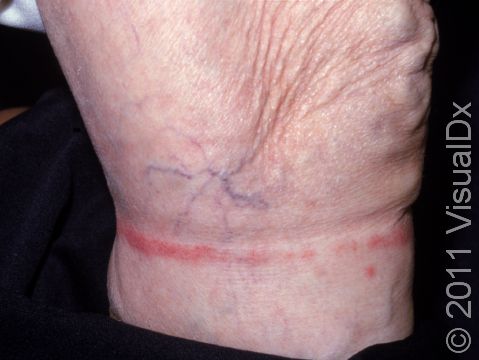
- Nickel is found in jewelry, belt buckles, metal closures on clothing, and some cell phones.
- Chromates are used in the process of tanning leather for shoes and in cement, so they can affect construction workers who are in contact with cement, for example.
- Rubber chemicals are found in gloves, balloons, elastic in garments, mouse pads, and swim goggles.
- Neomycin is common in triple antibiotic first aid ointments such as Neosporin (and generic versions of Neosporin) as well as other combination preparations with other antibacterials (eg, Polysporin). It may also be found in eye preparations and eardrops. Bacitracin is a common ingredient in antibiotic ointments and creams and can cause allergic contact dermatitis as well.
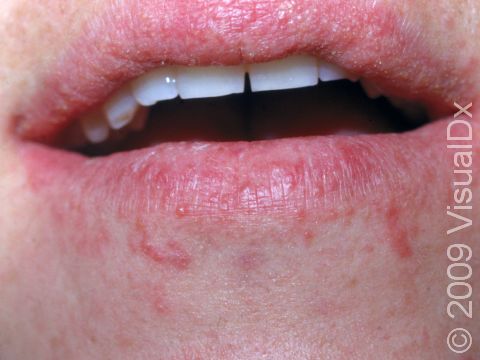
- Common allergen-containing products include sunscreens (oxybenzone [benzophenone-3]), cosmetics, soaps, dyes, and jewelry.
- Poison ivy is a frequent cause and is discussed separately.
Who's At Risk?
Allergic contact dermatitis can occur at any age in people of all races / ethnicities. Individuals with an existing skin condition (such as stasis dermatitis) requiring frequent application of topical agents can develop allergic contact dermatitis over time.
Signs & Symptoms
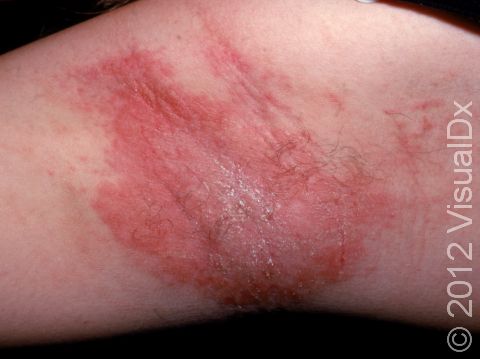
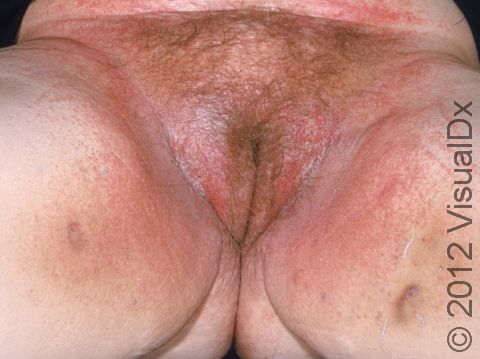
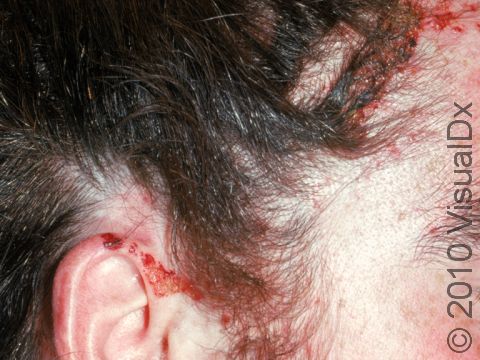
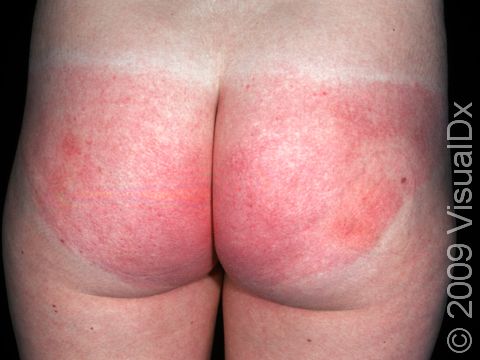
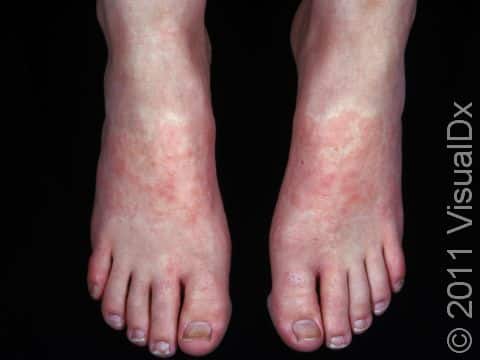
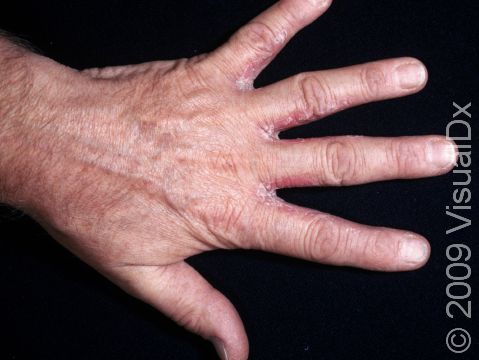
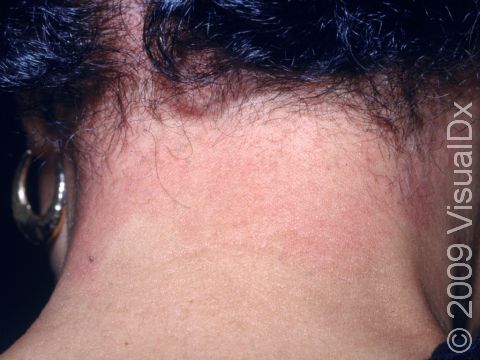
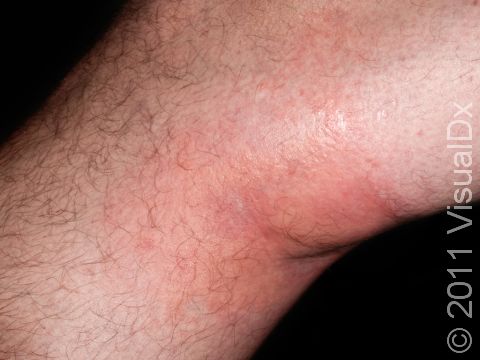
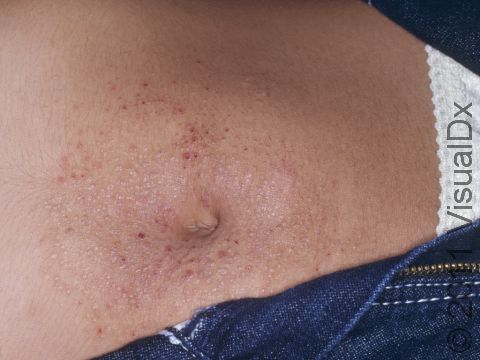
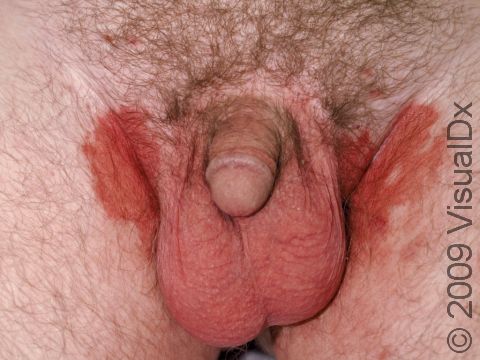
Allergic contact dermatitis may occur on any location of the body.
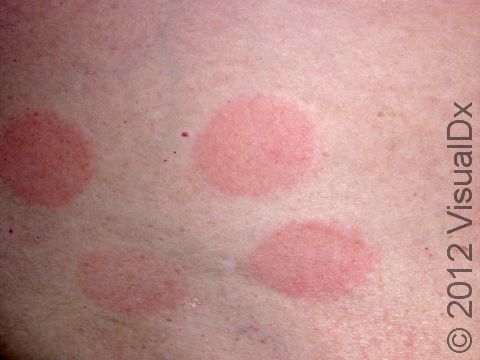
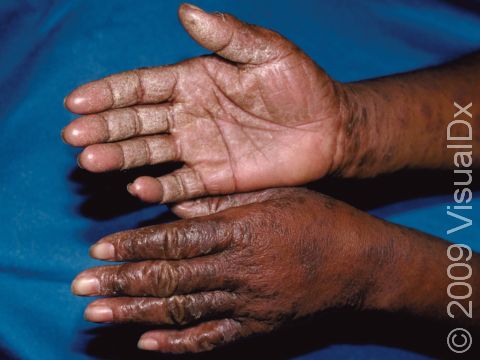
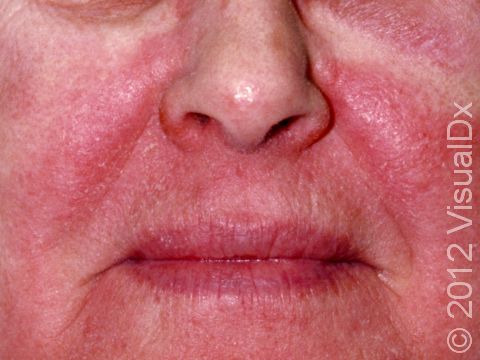
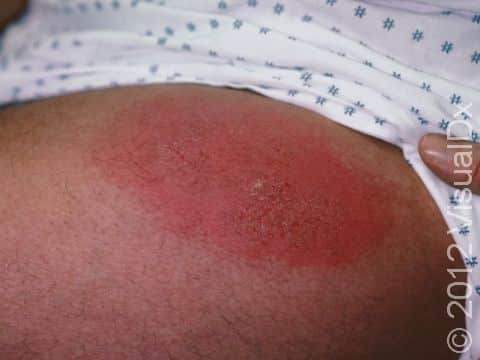
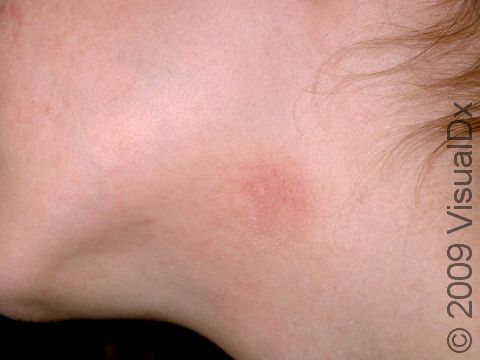
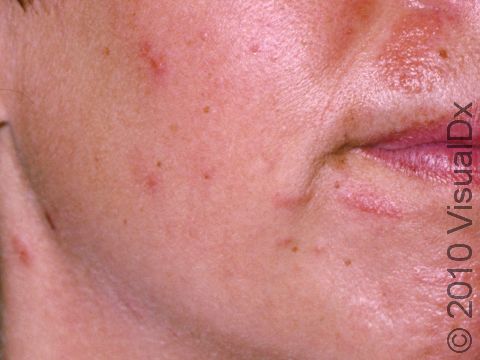
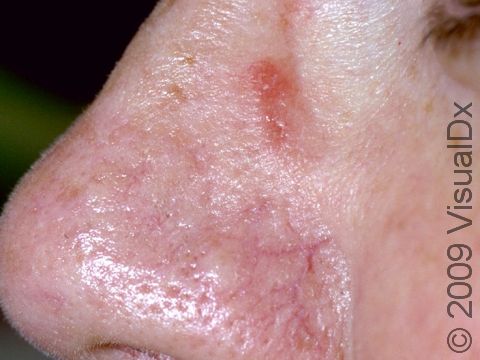
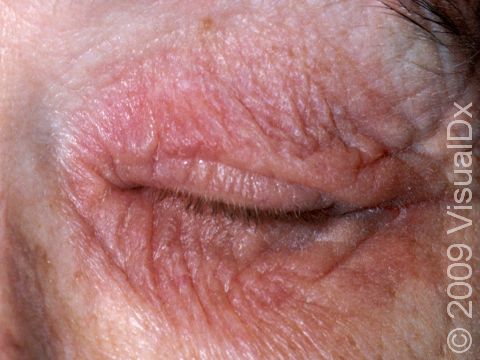
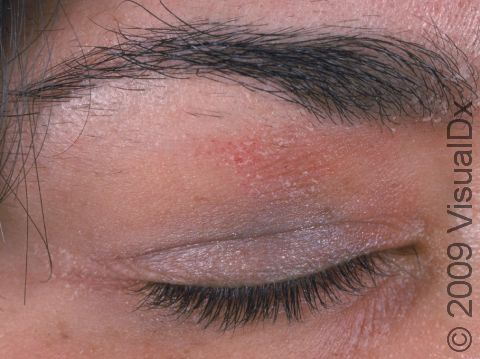
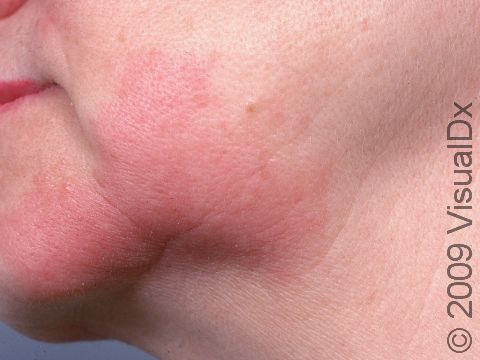
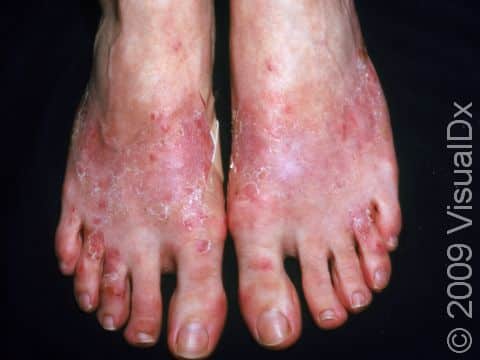
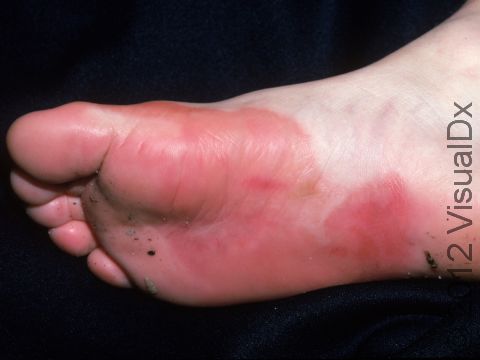
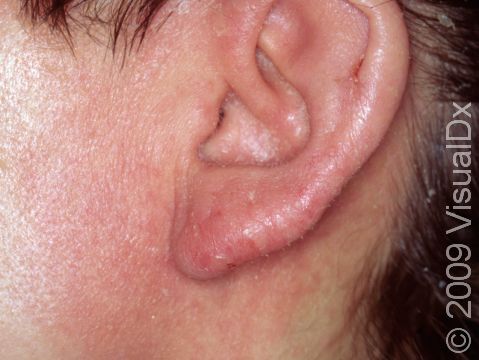
The affected areas of skin can look different on different body areas and on different people. There is often redness or other skin color changes, and there may be vesicles or bullae (blisters of different sizes), oozing, and crusting. Or there may be scaly plaques (elevated areas larger than a thumbnail). The lesions may have distinct borders with straight edges and sharp angles. In lighter skin colors, the areas are often pink or red, and in darker skin colors, the redness may be harder to see or may look more purple or gray.
Affected areas are typically severely itchy.
Eyelid swelling is frequently seen when the allergen is unknowingly transferred from finger to the eyelid.
When the dermatitis is chronic, the elevated areas can become thickened. Scratching the skin can cause cracks that may become infected with bacteria.
Self-Care Guidelines
- Ideally, you should avoid the allergen, if known.
- If you’re not sure what caused the allergic contact dermatitis or if you are prone to allergies or have sensitive skin, it may be helpful to avoid common triggers, such as fragrance, lanolin, nickel, etc. The American Contact Dermatitis Society’s Contact Allergen Management Program (CAMP) and SkinSAFE can help you find products that are free of identified allergens.
- Applying 1% over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream to the affected areas can be helpful in mild cases. Avoid using topical antihistamines, such as Benadryl lotion, as these may irritate the skin. Avoid topical antibiotics containing the common allergens bacitracin and neomycin.
Treatments
Treatment is aimed at preventing contact with the allergen.
Your medical professional may prescribe:
- An oral antihistamine to help control the itching.
- Low-potency topical steroids for thinner skin, such as on the face and skin folds.
- A medium-to-high-potency topical steroid for rashes occurring on the arms or legs or on the trunk (areas of the body with thicker skin).
- A course of an oral steroid (eg, prednisone) in severe cases involving large body areas.
Visit Urgency
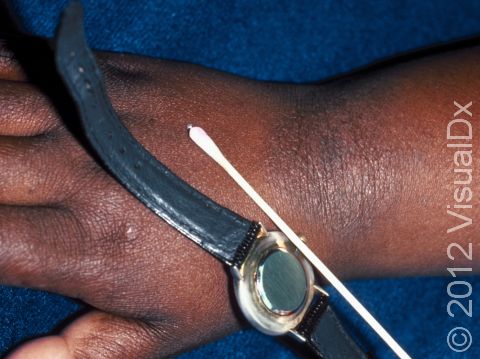
Seek medical evaluation for a persistent or recurrent rash of unknown origin. Your medical professional may perform patch testing (application of a series of chemicals under patches, usually applied to the back and left on for 48 hours) to check for potential contact allergies. A skin biopsy is sometimes used to confirm the diagnosis.
Trusted Links
References
Bolognia J, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018.
James WD, Elston D, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA. Andrew’s Diseases of the Skin. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019.
Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, et al. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education; 2019.
Last modified on June 17th, 2024 at 11:29 am
Not sure what to look for?
Try our new Rash and Skin Condition Finder