Discoid Lupus Erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus, often simply called lupus, is a chronic inflammatory disease that can affect almost any part of the body, especially the skin, joints, kidneys, heart, lungs, bones, blood, or brain. Lupus is considered an autoimmune disorder, meaning that a person’s own immune system attacks their healthy cells and tissues, causing inflammation and damage. The cause of lupus is unknown, but it may run in families, so it is thought that there is a genetic component.
Discoid lupus erythematosus is a form of lupus that affects the skin. About 5%-10% of people with discoid lupus erythematosus will progress to systemic lupus erythematosus.
Who's At Risk?
Discoid lupus erythematosus most commonly affects adult women, especially those in their 20s and 30s, and especially individuals of African and Hispanic descent. However, lupus may occur at any age, and it occurs worldwide. Lupus sometimes runs in families.
Signs & Symptoms
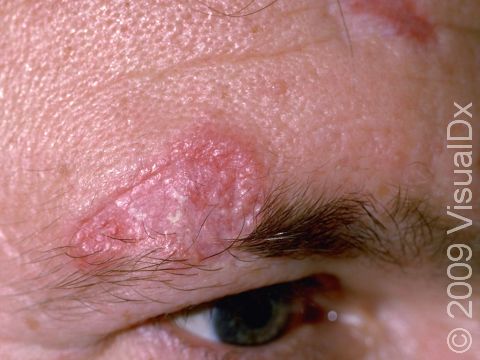
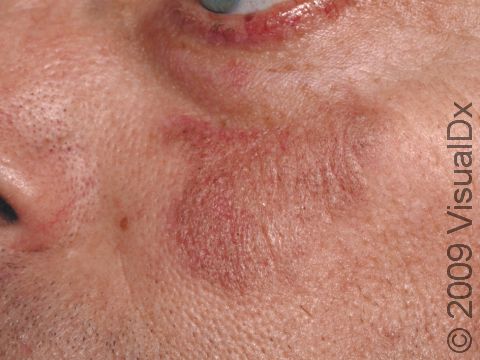
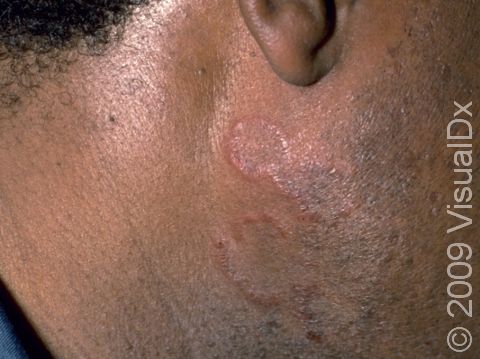
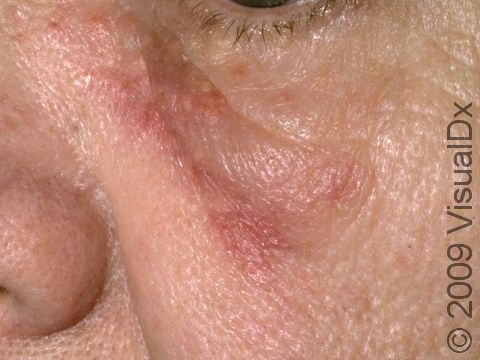
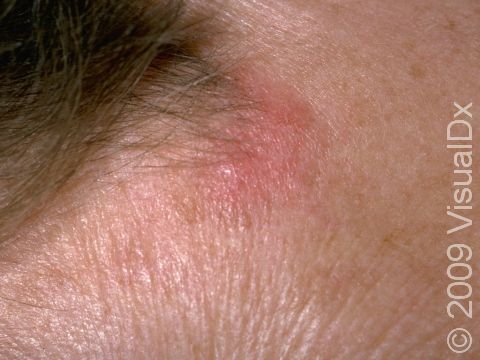
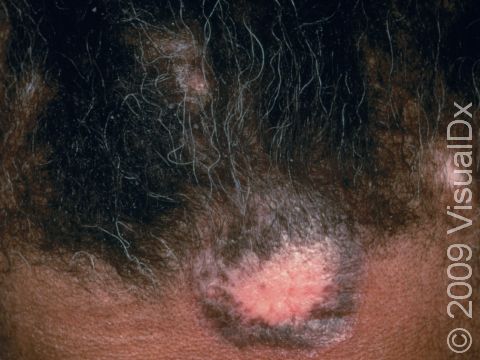
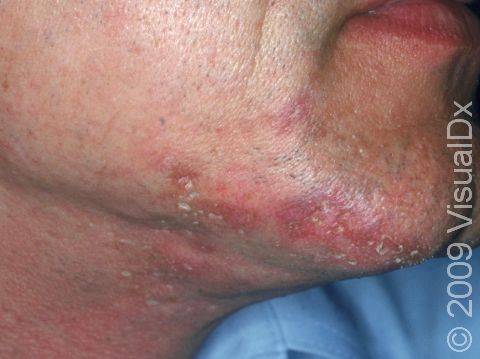
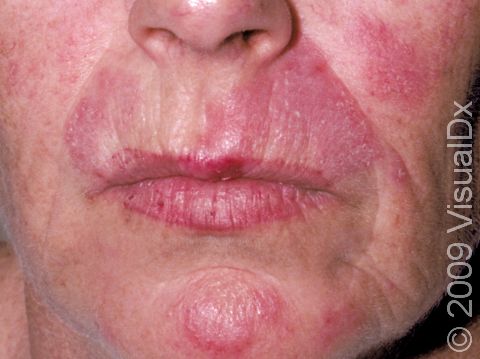
The skin lesions of discoid lupus erythematosus may vary in appearance. There may initially be a plaque (a raised area larger than a thumbnail) that is usually painless or only slightly itchy. In darker skin colors, the plaque may be red, or it may appear pink, maroon, purple, or brown. In lighter skin colors, the area may be any shade of pink or red. The area may be scaly or even wart-like. With time, the skin in the affected area becomes scarred, and if so, there may also be permanent hair loss, especially seen when lupus affects hair-bearing regions such as the scalp.
The lesions often (but not necessarily) occur in sun-exposed areas. The face, including the bridge of the nose, cheeks, lower lip, and ears, and the scalp are most often affected. Sometimes the trunk and the arms and legs are involved. The inside of the mouth can also be affected.
Self-Care Guidelines
To help prevent discoid lupus erythematosus flares:
- Wear sunscreen with UVB and UVA (ie, broad spectrum) blockers. Examples include CeraVe Hydrating Mineral Sunscreen SPF 50 with zinc oxide, CeraVe AM Face Moisturizing Lotion with Broad Spectrum SPF 30, Neutrogena Ultra Sheer Sunscreen SPF 50, and CeraVe Hydrating Mineral Sunscreen Body Lotion with Broad Spectrum SPF 50.
- Wear protective clothing (eg, dark colors with closely woven fabrics and hats), and avoid sun exposure.
- Avoid excessive heat, excessive cold, and trauma to the affected regions as these may make the condition worse.
- Avoid smoking.
Using cosmetics such as Covermark or Dermablend can help cover affected areas.
Consult the Lupus Foundation of America for more resources.
Treatments
Your medical professional may conduct blood tests and a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment your medical professional provides can improve the appearance of lesions, prevent new lesions, and prevent permanent hair loss and scars.
Your medical professional may prescribe:
- Topical corticosteroids.
- Topical immunosuppressive agents such as tacrolimus ointment.
- Antimalarial medications (hydroxychloroquine, chloroquine, or quinacrine) for severe cases.
- Other oral medications, which may include dapsone, acitretin, isotretinoin, thalidomide, and others.
Your medical professional may also recommend injections of corticosteroids into the affected skin.
Visit Urgency
Because discoid lupus erythematosus can cause permanent scars, including permanent hair loss, seek medical care if you suspect you may have this condition. Additionally, it is important to seek medical care to make sure discoid lupus is not a presenting sign of underlying systemic lupus.
Trusted Links
References
Bolognia J, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018.
James WD, Elston D, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA. Andrew’s Diseases of the Skin. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019.
Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, et al. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education; 2019.
Last modified on June 18th, 2024 at 8:23 am
Not sure what to look for?
Try our new Rash and Skin Condition Finder